- Automotive Hard Silver Plating
- Energy Storage Connector
- Cable Harness Connector
- EV Charging Connector
- Electric Bike Charging Cable
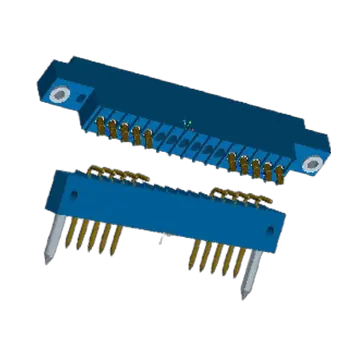
- PCB Connectors
- EV Charging Equipment
- High Voltage Wiring Harness
- Charging Socket
- Adapter EV Charging
- AUPINS POWER Charge Pro
- EV Cable Harness Ultrasonic Welding
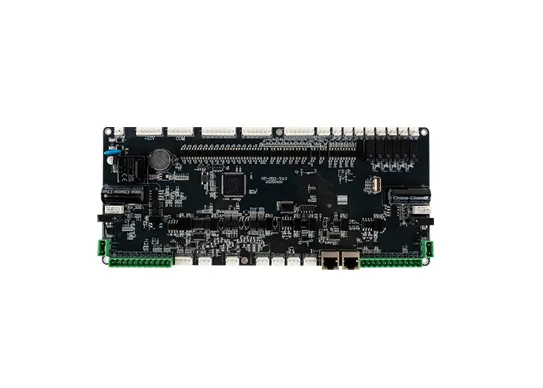
- EV Charge Control Board
- EV Charge Transformer
- ON BOARD CHARGER
-
 Brass Connector Pin For IEC EV Charging Plug
Brass Connector Pin For IEC EV Charging Plug
-
 Contact Pins For Sae EV Charging Plug
Contact Pins For Sae EV Charging Plug
-
 Charging Pin Connector For GB/T EV Charging Plug
Charging Pin Connector For GB/T EV Charging Plug
-
 NACS Connector Pin For Tesla EV Charging Plug
NACS Connector Pin For Tesla EV Charging Plug
-
 Lamella Contact Pins
Lamella Contact Pins
-
 Hyperboloid Contacts
Hyperboloid Contacts
-
 Crown Spring Pins
Crown Spring Pins
-
 Energy Storage Socket Connector
Energy Storage Socket Connector
-
 Energy Storage Plug Connector
Energy Storage Plug Connector
-
 SS1 Series Connector for Energy Storage Connector
SS1 Series Connector for Energy Storage Connector
-
 SS2 Series Connector for Energy Storage Connector
SS2 Series Connector for Energy Storage Connector
-
 Custom Cable Harness Assembling
Custom Cable Harness Assembling
-
 Wiring Harness Connector
Wiring Harness Connector
-
 EN50620 Cables
EN50620 Cables
-
 Electric Vehicle Charging Cable
Electric Vehicle Charging Cable
-
 Elevator & Conveyor Cable
Elevator & Conveyor Cable
-
 Industrial Cables And Wires
Industrial Cables And Wires
-
 AC Charging Connector
AC Charging Connector
-
 DC Charging Connector
DC Charging Connector
-
 Type 2 Open End Charging Cable
Type 2 Open End Charging Cable
-
 Type 2 -Type 2 Charging cable
Type 2 -Type 2 Charging cable
-
 CHAdeMo Connector
CHAdeMo Connector
-
 GB/T DC Charging Connector
GB/T DC Charging Connector
-
 NACS Vehicle Plug
NACS Vehicle Plug
-
 16 Core PCB Connectors
16 Core PCB Connectors
-
 AUPINS Pogopin Hypertac Hyperboloid Contact
AUPINS Pogopin Hypertac Hyperboloid Contact
-
 AUPINS Server Hashrate AI PCB Power Supply High Current Charging Terminal Pin
AUPINS Server Hashrate AI PCB Power Supply High Current Charging Terminal Pin
-
 Mode 2 GBT Portable EV Charger
Mode 2 GBT Portable EV Charger
-
 J1772 SAE Type 1 Portable EV Charger
J1772 SAE Type 1 Portable EV Charger
-
 IEC62196 Type 2 Portable EV Charger
IEC62196 Type 2 Portable EV Charger
-
 DC EV Charger
DC EV Charger
-
 AC Socket Cable(AC Socket→Battery)
AC Socket Cable(AC Socket→Battery)
-
 PDU Cable(Battery→Motor)
PDU Cable(Battery→Motor)
-
 Motor Wire
Motor Wire
-
 PTC Cable(Battery→Air Conditioner)
PTC Cable(Battery→Air Conditioner)
-
 DC Socket Cable(DC Socket→Battery)
DC Socket Cable(DC Socket→Battery)
-
 Ground Wire
Ground Wire
-
 Three Phase Power Line
Three Phase Power Line
-
 Air Pump Line→Compressor
Air Pump Line→Compressor
-
 CHAdeMO DC Charging Socket
CHAdeMO DC Charging Socket
-
 GB/T AC Charging Socket
GB/T AC Charging Socket
-
 GB/T AC Electronic Lock
GB/T AC Electronic Lock
-
 GB/T DC Charging Socket
GB/T DC Charging Socket
-
 SAE AC Charging Socket
SAE AC Charging Socket
-
 CCS1 DC Charging Socket
CCS1 DC Charging Socket
-
 IEC AC Charging Socket
IEC AC Charging Socket
-
 CCS2 Charging Socket
CCS2 Charging Socket
-
 IEC Electronic Sockets
IEC Electronic Sockets
-
 NACS Vehicle Charging Socket
NACS Vehicle Charging Socket
-
 AUPINS A5 Series Portable EV Charger
AUPINS A5 Series Portable EV Charger
-
 AUPINS C5 Series AC Wall-mounted Charger
AUPINS C5 Series AC Wall-mounted Charger
-
 AUPINS EF040 Series Public DC Fast EV Charger
AUPINS EF040 Series Public DC Fast EV Charger
-
 AUPINS EF160 Series DC Fast Charger
AUPINS EF160 Series DC Fast Charger
-
 AUPINS EF400 series 360 kw/400kw Public DC Quick Charger
AUPINS EF400 series 360 kw/400kw Public DC Quick Charger
-
 AUPINS S Series Type 2 IEC 62196 Charging Cable
AUPINS S Series Type 2 IEC 62196 Charging Cable
-
 AUPINS T3 Series Portable Charger Mode2 Pro
AUPINS T3 Series Portable Charger Mode2 Pro
WHAT ARE YOU LOOKING FOR?